NETA ATS
7.1 Switchgear and Switchboard
Assemblies
A. Visual and Mechanical
Inspection:
- Compare equipment nameplate data with drawings and specifications.
- Inspect the components for damage and errors in polarity or conductor routing.
- Verify that ground connection is made on the source side of the neutral disconnect
link and on the source side of any ground fault sensor.
- Verify that the neutral sensors are connected with correct polarity on both primary and
secondary.
- Verify that all phase conductors and the neutral pass through the sensor in the same
direction for zero sequence systems.
- Verify that grounding conductors do not pass through the zero sequence sensors.
- Verify that the grounded conductor is solidly grounded.
- Verify the unit is clean.
- Inspect bolted electrical connections for high resistance using one or more of the following
methods:
- Use of low-resistance ohmmeter in accordance with Section 7.14.B.1.
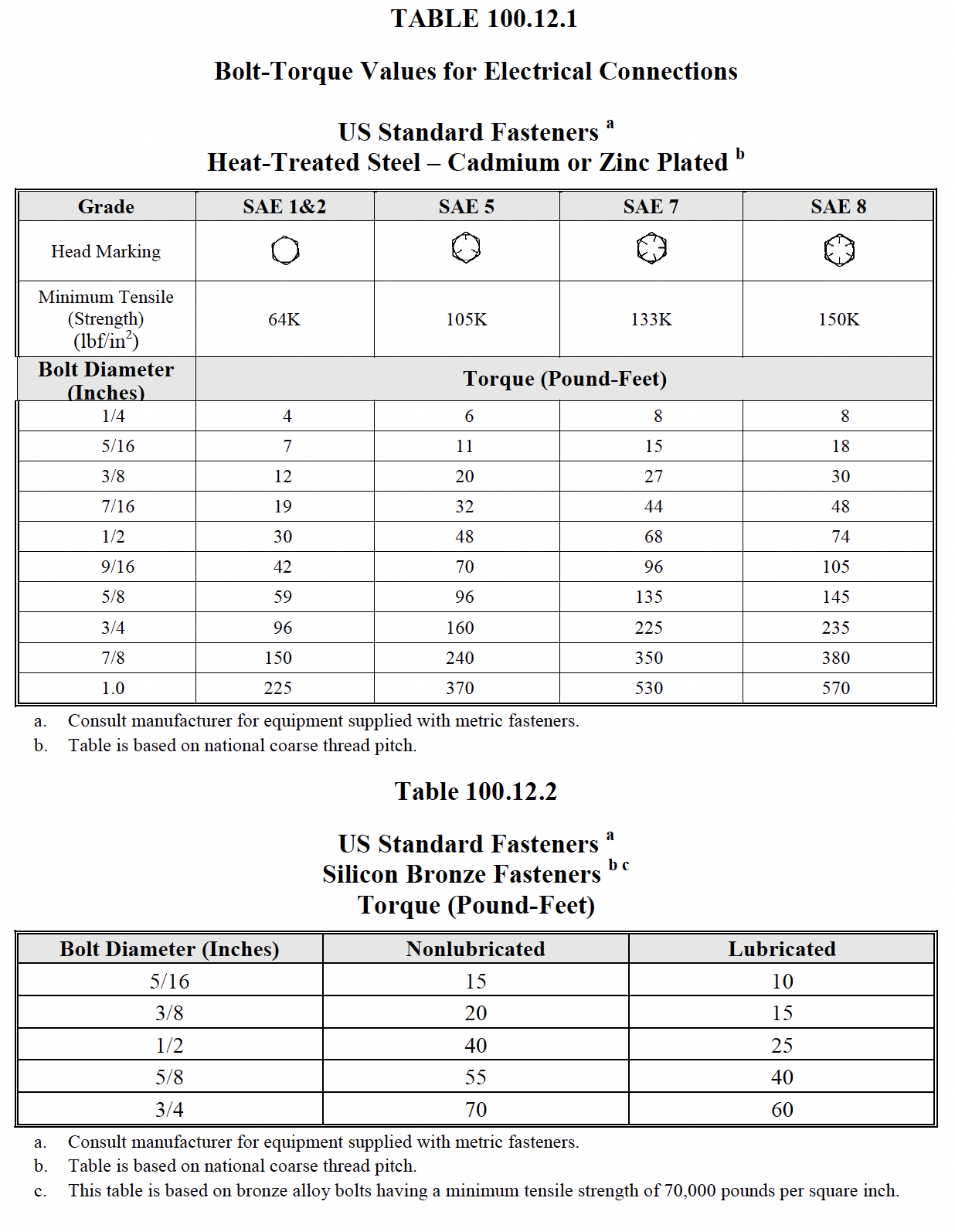
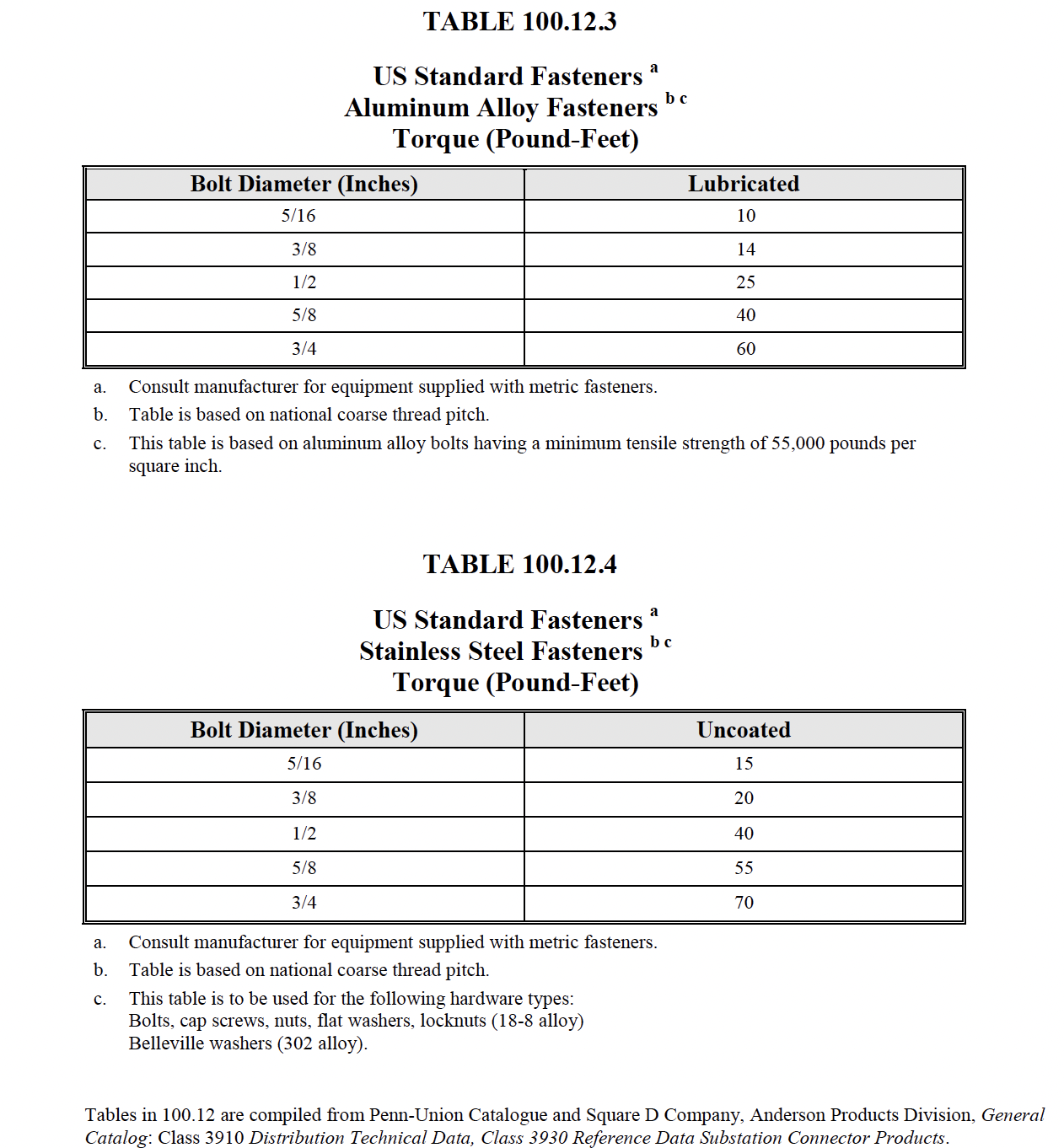
- Verify tightness of accessible bolted electrical connections by calibrated torquewrench
method in accordance with manufacturer’s published data or Table 100.12.
- Verify correct operation of all functions of the self-test panel, if applicable.
- Verify that the control power transformer has adequate capacity for the system.
- Set pickup and time-delay settings in accordance with the settings provided in the owner’s
specifications. Record appropriate operation and test sequences as required by NFPA 70,
National Electrical Code, Article 230.95.
B. Electrical Tests:
- Perform resistance measurements through bolted connections with a low-resistance
ohmmeter, if applicable, in accordance with Section 7.14.A.4.1.
- Measure the system neutral-to-ground insulation resistance with the neutral disconnect link
temporarily removed. Replace the neutral disconnect link after testing.
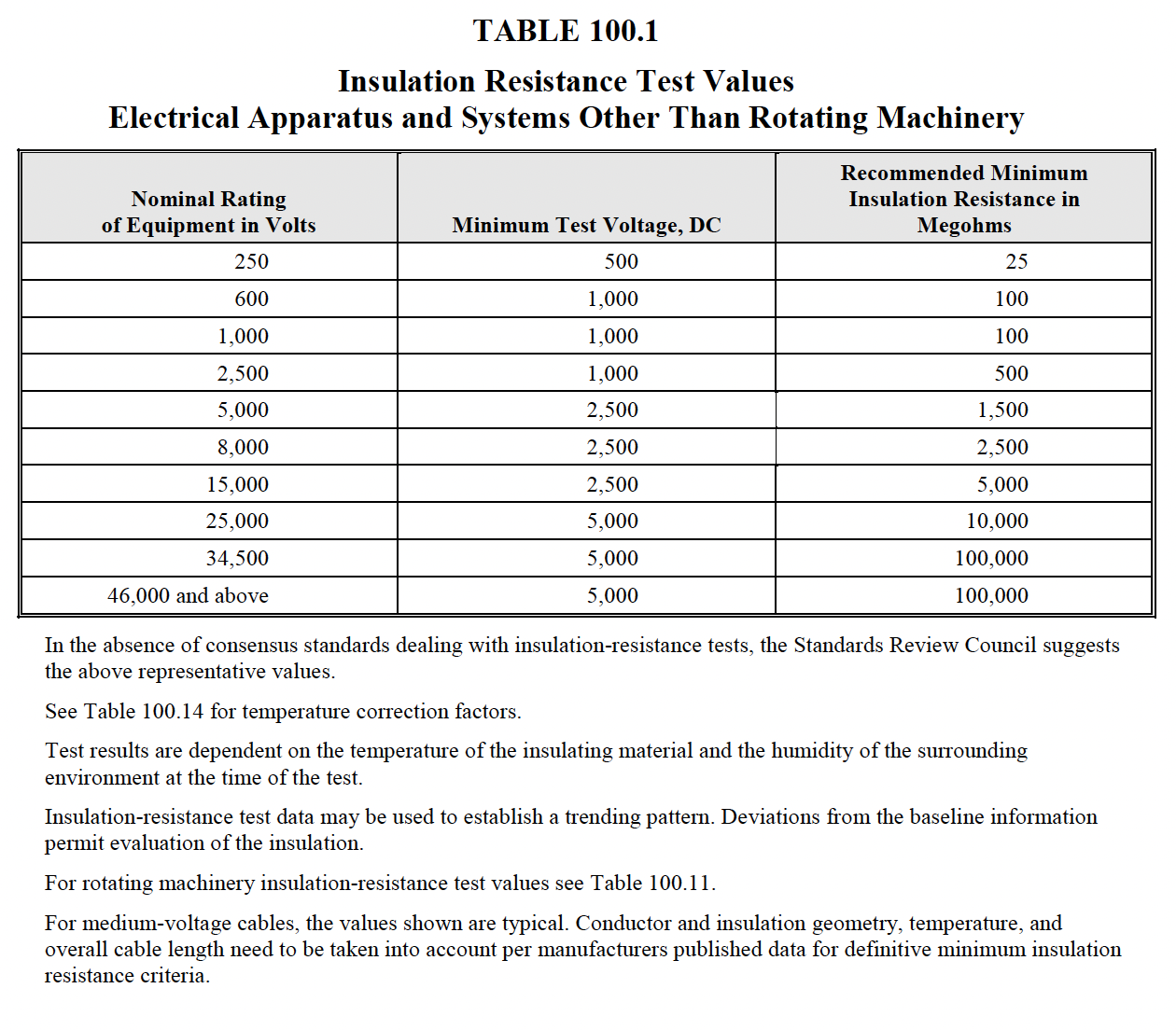
- *Perform insulation resistance test on all control wiring with respect to ground. Applied
potential shall be 500 volts dc for 300-volt rated cable and 1000 volts dc for 600-volt rated
cable. Test duration shall be one minute. For units with solid-state components or control
devices that cannot tolerate the applied voltage, follow manufacturer’s recommendation.
- Perform ground fault protective device pickup tests using primary injection.
- For summation type systems utilizing phase and neutral current transformers, verify correct
polarities by applying current to each phase-neutral current transformer pair. This test also
applies to molded-case breakers utilizing an external neutral current transformer.
- Measure time delay of the ground fault protective device at a value equal to or greater than
150 percent of the pickup value.
- Verify reduced control voltage tripping capability is 55 percent for ac systems and 80 percent
for dc systems.
- Verify blocking capability of zone interlock systems.
C. Test Values – Visual and
Mechanical
- values which deviate from those of similar bolted connections by more than 50 percent of the
lowest value. (7.14.A.4.1)
- Bolt-torque levels shall be in accordance with manufacturer’s published data. In the absence
of manufacturer’s published data, use Table 100.12. (7.14.A.4.2)
D. Test Values – Electrical
- values which deviate from those of similar bolted connections by more than 50 percent of the
lowest value.
- System neutral-to-ground insulation resistance shall be a minimum of one megohm.
- Insulation-resistance values of control wiring shall not be less than two megohms.
- Results of pickup test shall be greater than 90 percent of the ground fault protection device
pickup setting and less than 1200 amperes or 125 percent of the pickup setting, whichever is
smaller.
- The ground fault protective device shall operate when current direction is the same relative to
polarity marks in the two current transformers. The ground fault protective device shall not
operate when current direction is opposite relative to polarity marks in the two current
transformers.
- Relay timing shall be in accordance with manufacturer’s published data but must be no
longer than one second at 3000 amperes in accordance with ANSI/NFPA 70, National
Electrical Code, Article 230.95.
- The circuit interrupting device shall operate when control voltage is 55 percent of nominal
voltage for ac circuits and 80 percent of nominal voltage for dc circuits.
- Results of zone-blocking tests shall be in accordance with manufacturer’s published data and
design specifications.
NETA MTS
7.14 Ground-Fault Protection
Systems, Low-Voltage
A. Visual and Mechanical
Inspection:
- Inspect the components for damage and errors in polarity or conductor routing.
- Verify that the ground connection is made on the source side of the neutral
disconnect link and also on the source side of any ground fault sensor.
- Verify that the neutral sensors are connected with correct polarity on both primary
and secondary.
- Verify that all phase conductors and the neutral pass through the sensor in the same
direction for zero sequence systems.
- Verify that grounding conductors do not pass through the zero sequence sensors.
- Verify that the grounded conductor is solidly grounded.
- Prior to cleaning the unit, perform as-found tests.
- Verify the unit is clean.
- Inspect bolted electrical connections for high resistance using one or more of the following
methods:
- Use of low-resistance ohmmeter in accordance with Section 7.14.B.1.
- Verify tightness of accessible bolted electrical connections by calibrated torquewrench
method in accordance with manufacturer’s published data or Table 100.12.
- Verify correct operation of all functions of the self-test panel.
- Verify pickup and time-delay settings in accordance with the settings provided in the
owner’s specifications. Record appropriate operation and test sequences as required by
NFPA 70 National Electrical Code, Article 230.95.
- perform as-left tests.
B. Electrical Tests:
- Perform resistance measurements through bolted connections with a low-resistance
ohmmeter in accordance with Section 7.14.A.4.1.
- Measure the system neutral-to-ground insulation resistance with the neutral disconnect link
temporarily removed. Replace neutral disconnect link after testing.
- *Perform insulation-resistance tests on all control wiring with respect to ground. The applied
potential shall be 500 volts dc for 300-volt rated cable and 1000 volts dc for 600-volt rated
cable. Test duration shall be one minute. For units with solid-state components or control
devices that cannot tolerate the applied voltage, follow manufacturer’s recommendation.
- Perform ground fault protective device pickup tests using primary current injection.
- For summation type systems utilizing phase and neutral current transformers, verify correct
polarities by applying current to each phase-neutral current transformer pair. This test also
applies to molded-case breakers utilizing an external neutral current transformer.
- Measure time delay of the ground fault protective device at a value equal to or greater than
150 percent of the pickup value.
- Verify that reduced control voltage tripping capability is 55 percent for ac systems and 80
percent for dc systems.
- Verify blocking capability of zone interlock systems.
C. Test Values – Visual and
Mechanical
- Compare bolted connection resistance values to values of similar connections. Investigate
values which deviate from those of similar bolted connections by more than 50 percent of
the lowest value. (7.14.A.4.1)
- Bolt-torque levels should be in accordance with manufacturer’s published data. In the
absence of manufacturer’s published data, use Table 100.12. (7.14.A.4.2)
D. Test Values – Electrical
- Compare bolted connection resistance values to values of similar connections. Investigate
values which deviate from those of similar bolted connections by more than 50 percent of
the lowest value.
- System neutral-to-ground insulation resistance should be a minimum of one megohm.
- Insulation-resistance values of control wiring should be comparable to previously obtained
results but not less than two megohms.
- Results of pickup test should be greater than 90 percent of the ground fault protection
device pickup setting and less than 1200 amperes or 125 percent of the pickup setting,
whichever is smaller.
- The ground fault protective device should operate when current direction is the same
relative to polarity marks in the two current transformers. The ground fault protective
device should not operate when current direction is opposite relative to polarity marks in the
two current transformers.
- Relay timing should be in accordance with manufacturer’s specifications but must be no
longer than one second at 3000 amperes in accordance with NFPA 70, National Electrical
Code, Article 230.95.
- The circuit interrupting device should operate when control voltage is 55 percent of nominal
voltage for ac circuits and 80 percent of nominal voltage for dc circuits.
- Results of zone-blocking tests should be in accordance with manufacturer’s published data
and/or design specifications.
|