| Arc Flash Hazard Analysis Report | |
|---|---|
| Arc Flash Hazard Analysis Report: |
An Arc Flash Assessment / Analysis is a study of a facility’s power system. Its purpose is to determine the available incident energy values at specific locations where personel would "interact" or be exposed to live or energized electrical equipment.
Image
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet consectetur, adipisicing elit. Voluptatibus et, consequatur perspiciatis temporibus eius repellat, est architecto magnam assumenda cumque praesentium. What is the purpose of an Arc Flash Study?To determin the protective clothing requirements for persons working on live gear. Are Electrical Engineers required to perform an Arc Flash Study?Yes, Per NEC Article 110.16, "...maintenace while energized shall be field or factory marked to warn qualified persons of potential electrical arc flash hazards" what are good references for engineers performing arc flash studies?
What are the industry standard calculation methods currently in use?
|
| SHORT CIRCUIT ANALYSIS: |
An electric arc or an arcing fault is the flow of electric current through the air from one conductor to another or to ground. Arcs are generally initiated by a flashover caused by some type of conductor that subsequently vaporizes or falls away, leaving an arc. Arcing faults create many hazards, but the greatest risk is burn injuries due to exposure to the heat generated by the arc. This heat can cause serious, even fatal burns, as well as ignite clothing and other nearby material and objects. In addition, electric arcs can produce molten metal droplets, UV radiation, and explosive air pressure waves. |
| PROTECTION COORDINATION: |
An electric arc or an arcing fault is the flow of electric current through the air from one conductor to another or to ground. Arcs are generally initiated by a flashover caused by some type of conductor that subsequently vaporizes or falls away, leaving an arc. Arcing faults create many hazards, but the greatest risk is burn injuries due to exposure to the heat generated by the arc. This heat can cause serious, even fatal burns, as well as ignite clothing and other nearby material and objects. In addition, electric arcs can produce molten metal droplets, UV radiation, and explosive air pressure waves. |
| PROTECTION COORDINATION: |
Our Company
At Themesberg, our mission has always been focused on bringing openness and transparency to the design process. We've always believed that by providing a space where designers can share ongoing work not only empowers them to make better products, it also helps them grow. We're proud to be a part of creating a more open culture and to continue building a product that supports this vision.
Neumorph Components
At Themesberg, our mission has always been focused on bringing openness and transparency to the design process. We've always believed that by providing a space where designers can share ongoing work not only empowers them to make better products, it also helps them grow. We're proud to be a part of creating a more open culture and to continue building a product that supports this vision. |
| SHORT CIRCUIT ANALYSIS: | |
|---|---|
| Utility Information: |
Utility Companies can provide a fault report for customers. The fault report has fault current valuesat the point of interconnection between the utility company and the customers meter. |
| Asymmetrical Current: |
Asymmetrical Current: The total current value including the symmetrical component and DC offset introduced during fault conditions. |
| Symmetrical Current: |
Symmetrical Current: The component of current where the magnitude of current is seen on positive and negative cycles, no DC offset. |
| DC Offset: |
DC Offset: The positive or negative offset of the AC waveform at the inception of a fault. The DC offset is at maximum when the fault occurs at the zero crossing of the driving voltage. Both the degree of offset and the duration of offset are determined by the system X/R ratio. |
| Series Rating: |
Series Rating: A tested combination of protective devices that allow the use of protective devices in locations that exceed the nameplate rating by operation of a main or upstream protecting devices. Operation of the series rated combination allows the devices to share the interrupting energies. |
| COORDINATION: | |
|---|---|
|
Our Company
At Themesberg, our mission has always been focused on bringing openness and transparency to the design process. We've always believed that by providing a space where designers can share ongoing work not only empowers them to make better products, it also helps them grow. We're proud to be a part of creating a more open culture and to continue building a product that supports this vision.
Neumorph Components
At Themesberg, our mission has always been focused on bringing openness and transparency to the design process. We've always believed that by providing a space where designers can share ongoing work not only empowers them to make better products, it also helps them grow. We're proud to be a part of creating a more open culture and to continue building a product that supports this vision. |
|
| Motor Nameplate Data | |
|---|---|
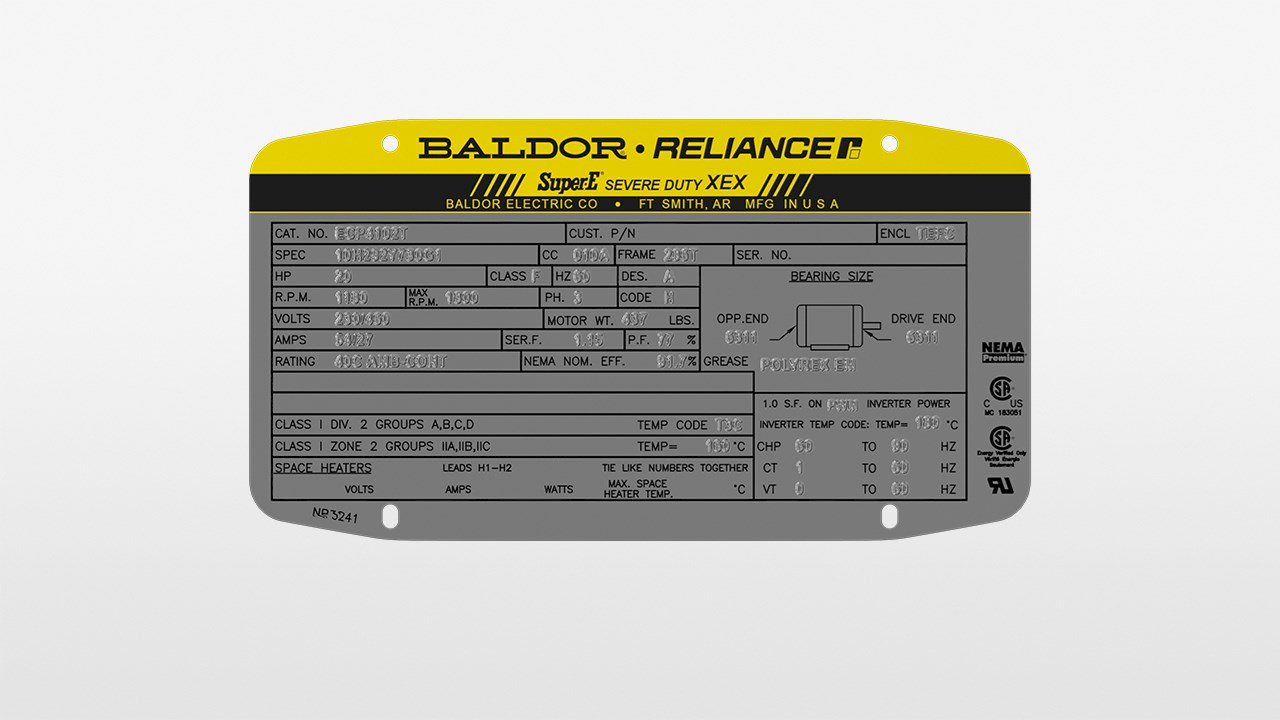
|
|
Definition of a Bus as it pertains to Short Circuit Calculations.
Definition of a Bus as it pertains to Short Circuit Calculations. The term Bus is taken from the IEEE 141, 241, and 399 standards where impedance diagrams are discussed. Impedance diagrams are used to facilitate short circuit calculations, whereby the connection point between two different impedance values is described as a bus. Very often, a bus represents the bus bar within a piece of switchgear, MCCs, Panels or other load points, however for \convenience of entry, additional buses are created between two cables, between cables and transformer so that each impedance component can be entered separately without manually calculating an equivalent impedance for a group of components.
Voltage Ratings:
- 120V, 208, 240V
- 480V, 600V
Efficiency
A motor’s efficiency rating measures how well the motor converts electrical energy (input) into mechanical energy (output). This is usually displayed as a decimal. A motor’s energy consumption is by far its largest operating expense. As a general rule, a motor that runs 24/7/365 for one year could cost three times more than the purchase price in power consumption. In many applications a VFD can provide considerable savings with regards to operational costs. Centrifugal pumps often have great potential for energy savings. Under some circumstances using a VFD to reduce speed by 20% can result in energy savings of 50%. However, energy savings will vary based upon several factors, such as motor conditions, application, and energy costs in your area.
| Transformer Inrush Current |
During the initial phase of energization, a transformer will pull a significantly larger than normal current. This Inrush current quickly settles into a lower operational value where it will remain until the transformer is re-energized. If the transformer’s inrush currents falls above the maximum instantaneous current rating of the protective device, this could potentially cause the device to trip. It is recommended that a circuit breaker with short time delay setting is used to allow enough time for the transformer’s inrush current to clear while maintaining acceptable arc flash risk levels. |
|---|---|
| Motor Inrush Current |
|
|---|---|
| Citations: | |
|---|---|
|
Bernstein, Mark. “10 Tips on Writing the Living Web.” A List Apart: For People Who Make Websites, 16 Aug. 2002, alistapart.com/article/writeliving. Accessed 4 May 2009. |
|
| Citations: | |
|---|---|
|
SKM System Analysis, Inc. “Intro 2 to SKM Power Tools, SKM Course 102” |
|


